Rylan Schaeffer

Resume
Publications
Learning
Blog
Teaching
Jokes
Kernel Papers
Engram cells retain memory under retrograde amnesia
by Ryan, Roy, Pignattelli, ..., Tonegawa (Science 2015)
Background
Memory consolidation is process by which a new memory transitions from a fragile state to a long-term stable state. For short time after learning, memory is susceptible to disruption e.g. by protein synthesis inhibitor (PSI), which can cause retrograde amnesia.
Disclaimer: This paper explains its experiments very poorly. Reading the supplement directly is highly recommended.
Research Questions
- How does retrograde amnesia (induced by PSI) interact with the formation and function of memory engrams?
Experiments
Exp 1 (Cellular)
- Take mice off Dox, perform contextual fear conditioning (CFC) and inject either saline or anisomycin (a protein synthesis inhibitor) into hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG)
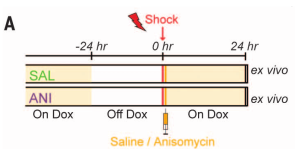
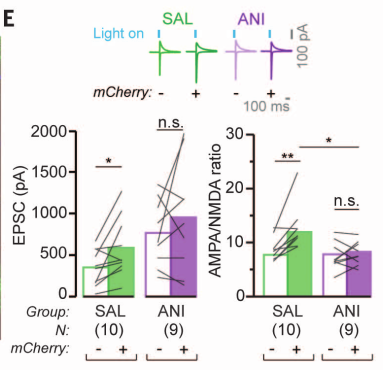
- Test synaptic strength by optogenetically activating tagged engram neurons (mCherry+) or non-engram neurons (mCherry-)
- mCherry+ neurons (engram neurons) had significantly stronger synapses in the saline condition but not in the anisomycin condition
- mCherry+ (engram) neurons had higher dendritic spine density in the saline condition than in the anisomycin condition
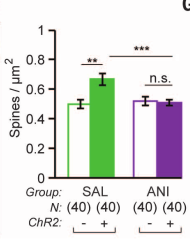
- Takeaway: Injecting anisomycin (ANI) into dentate gyrus after CFC impairs synaptic strengthening and dendritic density
Exp 2 (Behavioral)
- What is the behavioral effect of optogenetically stimulating engram cells in amnesic mice?
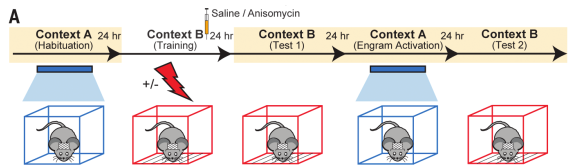
- For control, some mice not exposed to shock
- Freezing in decreasing order: saline + shock, anisomycin + shock, saline (no shock), anisomycin (no shock) (Fig 2C)
- Optogenetically activating DG neurons results in freezing behavior regardless of saline/anisomycin
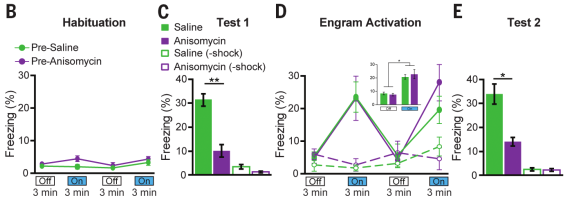
- Replicated using another PSI cycloheximide (CHM)
- Injecting ANI 24 hours later had no effect
- Authors: Recovery from amnesia through light activation of DG engram cells was unexpected because these cells showed neither synaptic potentiation nor increased dendritic spine density
Exp 3 (Behavioral)
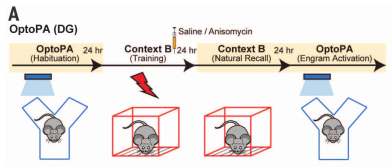
- Can recovery from amnesia can be demonstrated with light-induced optogenetic place avoidance test (OptoPA)?
- The below figure oversimplifies this experiment
- Mice placed in context with two “zones” and given 3 minutes to explore; the preferred zone became the “target zone”
- For minutes 3-6 and 9-12, turn on light whenever mouse enters the target zone
- Fear condition Context B, then immediately injecting saline or ANI into (can’t tell; my guess is dentate gyrus?). Use Dox diet to label the active neurons.
- Mice placed back in first context and given 3 minutes to explore; the preferred zone became the “target zone”
- During 3-6 minutes, 9-12 minutes, light was turned on
- Difference score := time in target zone without light - (time in target zone with light on minutes 3-6 + time in target zone with light on minutes 9-12) / 2
- ANI causes significantly less freezing than saline during natural recall
- Cells are equally activated during optogenetic
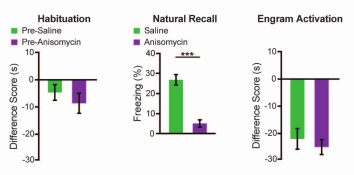
- Takeaway: Anisomycin in DG impairs natural fear recovery, but optogenetically activating those neurons retrieves the fear response in another context
Exp 4 (Behavioral)
- Skipping
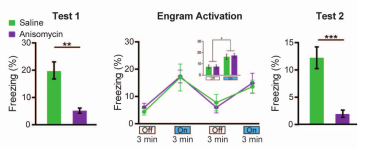
Exp 5 (Behavioral)
- Auditory fear conditioning.
- Same experimental setup as previous experiment, but replacing contexts with tones and injecting ANI or Saline into lateral amygdala
- Fear engram neurons were identified with Dox diet after Context B training

- Again, ANI reduced freezing of mouse to CS tone by 20%
- Again, activating engram in neutral Context A increased freezing comparable to saline group
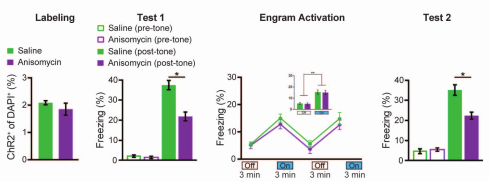
Exp 6 (Behavioral)
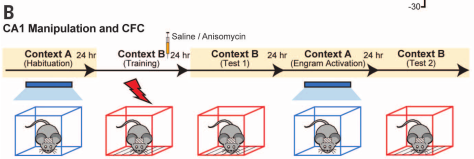
- Can amnesia caused by disruption of reconsolidation of CFC be recovered through light-activation of DG engram cells?
- Context A engram labeled, followed by injection of saline or anisomycin
- Mice fear conditioned in Context C, while light was activated
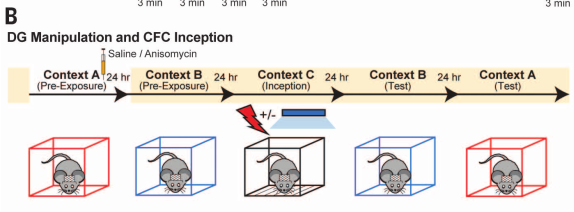
- Freezing to irrelevant context B remained low
- Mice acquired fear to Context A, with greater fear response in anisomycin context
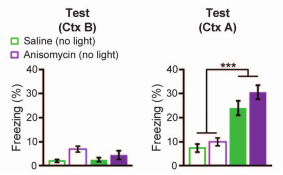
- Takeaway: Can create freezing response to forgotten context A by shocking context A dentate gyrus neurons while mouse in Context C
Exp 7 (Neural)
- How are basolateral amygdala and central amygdala involved in constructing fear memory?
- Label and activate Context A. Fear condition Context B, then inject saline or anisomycin. Test recall to Context B or Context A with DG activation
- Natural recall results in lower c-Fos+ cell counts for anisomycin, not saline, in both BLA and CeA
- Optogenetic activation of DG removes effect
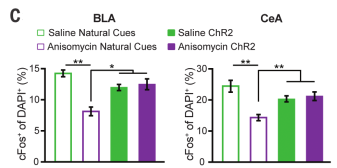
- Takeaway: BLA and CeA are more active either without anisomycin or with optogenetic stimulation