Rylan Schaeffer

Resume
Publications
Learning
Blog
Teaching
Jokes
Kernel Papers
Synapse-specific representation of the identity of overlapping memory engrams
by Abdou, ..., Inokuchi (Science 2018)
Research Questions
Previously, Rashid et al. 2016 and Cai et al. 2016 showed that conditioning close in time result in overlapping engrams, and Yokose et al. 2017 further showed that the overlap in neurons between engrams is responsible for linking the shared experiences. This paper asks and answers:
- How does the brain distinguish identity of particular memory amid many memories in the same ensemble? Answer: sensory engrams drive reactivation of the entangled engram
Experiments
Exp 1
- There are a lot of details here!
- Previous results showed plasticity between auditory cortex (AC), medial geniculate nucleus (MGn) and lateral amygdala (LA) is necessary for auditory fear conditioning
- Day 1-2: Auditory cue (2 kHz)
- Day 4: Fear conditioning (7 kHz)
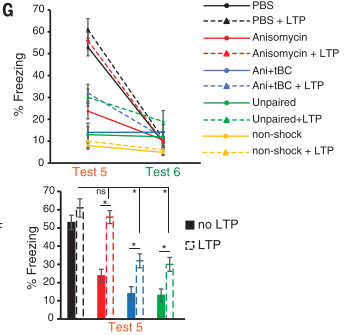
- Day 5: Test fear recall. Immediately after, mice injected with one of: saline (PBS), anisomycin (ani), anisomycin + tat-beclin (Ani+tBC)
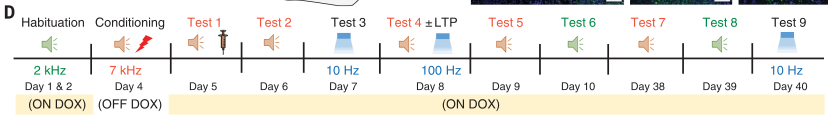
- Test 2: Ani resulted in partial retrograde amnesia; Ani+tBC resulted in complete retrograde amnesia (1E)
- Optogenetic activation of AC and MGn engram neurons with axons in LA induced fear recall in PBS and Ani gropus, but not Ani + tBC (consistent with prior results) (1F)
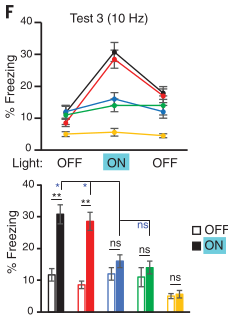
- Day 7: Try recovering AC & MGn synapses to LA with optogenetic stimulation
- Test 3: Ani group recovered to baseline (1G, left) whereas Ani+tBC did not (1G, left)
- Day 38-39 (test 7 & 8): Test fear retrieval. Ani + tBC remained low, comparable to unconditioned
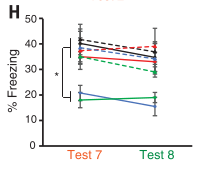
- Day 40 (test 9): Test fear retrieval with optogenetic stimulation. Ani + tBC + LTP on day 8 recovers association, but Ani + tBC does not.
- Same result if recall was tested using optogenetic activation instead of tone
- Takeaway: Ani + tBC prevents AC and MGn synapses from activating LA engram
Exp 2
- Don’t understand. Something about selective erasure of target memory.
Exp 3
- Don’t understand. Something about selective erasure of target memory.
Exp 4
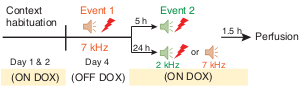
- What is effect of complete retrograde amnesia of one memory in shared engram ensemble?
- Fear condition 7-kHz (event 1). Then fear condition 2-kHz (event 2) either 5 hours or 24 hours later
-
When two events were separated by 5 hours, recall for event 2 was enhanced (fig. S5), consistent with Rashid 2016
-
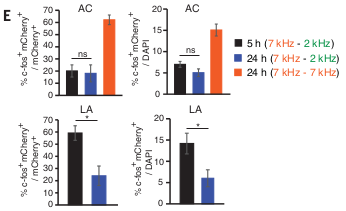
Regardless of 5h or 24h, two engrams were found in auditory cortex (3E top)
-
Overlap in lateral amygdala was significantly larger in 5h than 24h
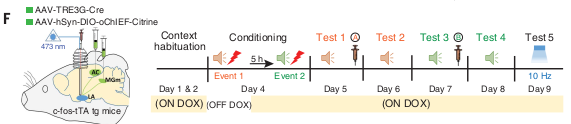
Exp 5
- Building off previous experiment, have two groups of mice go through two fear conditionings separated by 5 hours
- Group 1 has AC/MGn injected with saline after Event 1 test (Day 5), then AC/MGn injected with Ani+tBC after Event 2 test (Day 7)
- Group 2 has AC/MGn injected with Ani+tBC after Event 1 test (Day 5), then AC/MGn injected with saline after Event 2 test (Day 7)
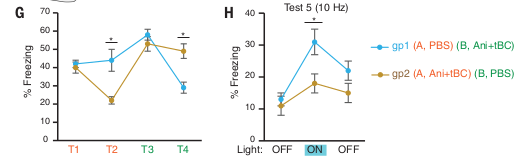
- Both groups correctly recall fear during first test to Tone A
- Group 1 unaffected during second test of Tone A, but Group 2 freezes significantly less (suggesting erasure of Fear 1)
- Both groups correctly recall fear during first test to Tone B
- Group 2 unafffected during second test of Tone B, but Group 1 freezes significantly less (suggesting erasure of Fear 2)
- Cartoon demonstrating selective erasure of synapses to shared engram. Yellow are two overlapping engrams in lateral amygdala
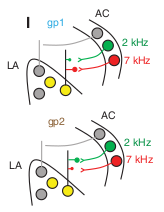
- Takeway: we can selectively erase synapses from sensory areas (auditory cortex, MGn) to lateral amygdala
- Rylan question: how do we know that Tone A fear is preserved in group 2?
Exp 6
- How is each memory preserved in the shared ensemble?
- Takeaway: sensory-engrams drive overlapping engrams, preserving uniqueness of memory
TODO: maybe finish later. this was a big let down
tags: memory-engrams - lateral-amygdala - auditory-fear-conditioning - conditioned-taste-aversion - optogenetics