Rylan Schaeffer

Resume
Publications
Learning
Blog
Teaching
Jokes
Kernel Papers
The role of neuronal excitability, allocation to an engram and memory linking in the behavioral generation of a false memory in mice
by Lau, ..., Josselyn (Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2020)
Background
Previously, Rashid et al. 2016 and Cai et al. 2016 showed that conditioning close in time result in overlapping engrams, and Yokose et al. 2017 further showed that the overlap in neurons between engrams is responsible for linking the shared experiences.
Research Questions
This paper asks and answers:
- Is creating a behavioral response to a false memory possible? Answer: Yes
- How does the behavioral response depend on elapsed time? Answer: 3 hours is possible, 24 hours is not.
Experiments
Exp 1 (Behavior)
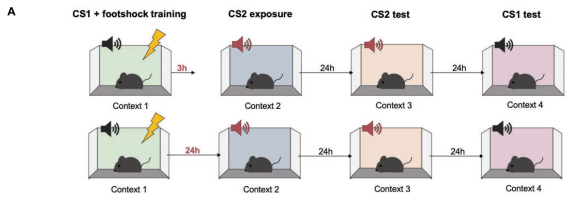
- Day 1: Fear condition Tone A. Then, either 3hr or 24hr later, present a neutral stimulus Tone B
- Day 2: Test Tone B
- Day 3: Test Tone A.
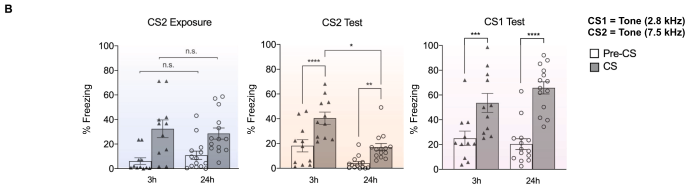
- Freezing in response to Tone B during first presentation is equal between 3h and 24 hr groups
- Freezing to Tone B during test is higher for 3h than 24 hr group
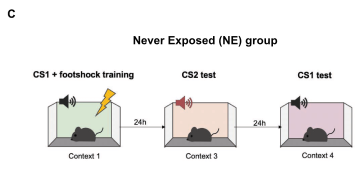
- For control, repeat experiment with no Tone B exposure.
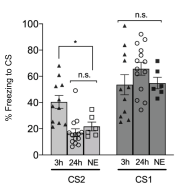
- Freezing (in decreasing order): Tone A > Tone B (3 hr) > Tone B (24 hours) = No Tone B exposure
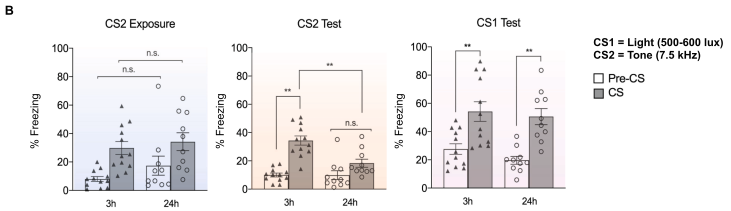
Exp 2 (Behavior)
- Repeat the same experiment, replacing the negative Tone A with negative Light A
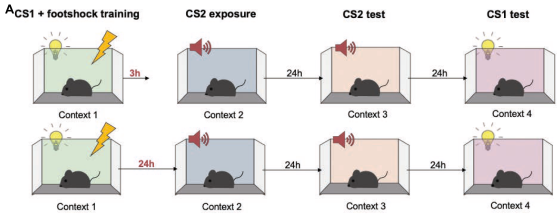
- Same results as before
- Freezing in response to Tone B during first presentation is equal between 3h and 24 hr groups
- Freezing during test (in decreasing order): Light A > Tone B (3 hr) > Tone B (24 hr)
Exp 3 (Neural)
- Later experiments will need to manipulate engrams in 3 hours. This is too short for the typical tag-and-manipulate approach, necessitating allocate-and-manipulate approach
- Consequently, need to test that allocate-and-manipulate is valid. Want to test that optogenetical manipulation increases probability of neurons being recruited to engram strategy
- Group 1: Use blue-light to activate specific neurons during fear conditioning. Use red light to inhibit those same neurons.
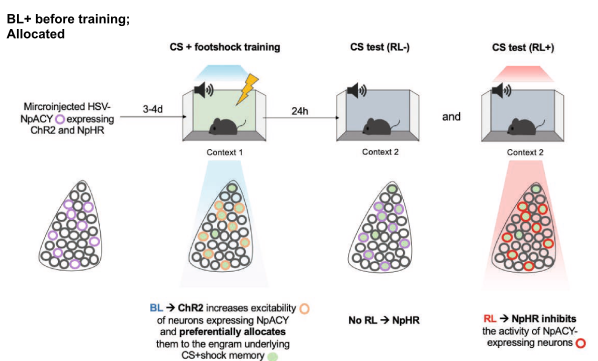
- Group 2: No blue-light to activate specific neurons during fear conditioning. Use red light to inhibit those same targeted neurons.
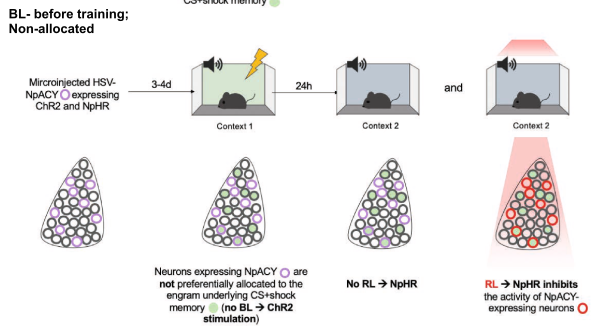
- Result: Group 1 freeze less when red light activated
- Takeaway: Optogenetic stimulation controllably biases which neurons are recruited to the engram
Exp 4 (Neural)
- Three conditions: auditory fear condition (FC), blue light with no fear conditioning (BL), blue light with fear conditioning (BL+FC)
- Measure c-fos+ immunohistochemistry (which I guess measures cell activity / synaptic formation)
- In targeted neurons, highest c-fos+ expression in BL+FC, then FC, then BL
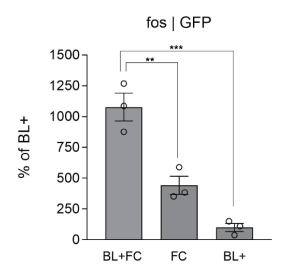
- Takeaway: further suggests that blue light biases which neurons are allocated to the memory engram
Exp 5 (Neural, Behavioral)
- THE BIG EXPERIMENT in this paper
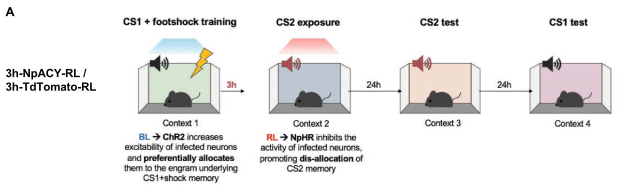
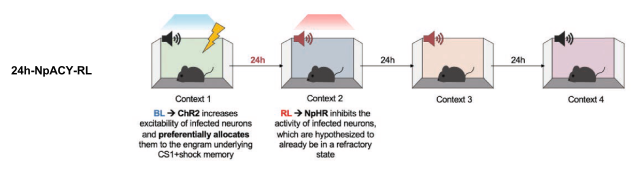
- Hypothesis: false association learnt if CS2 was presented 3 hours post conditioning because co-allocated to same engram
- Group 3h-NpACY-RL: Fear condition CS1 using blue light to bias preselected neurons towards inclusion in engram. 3 hours later, expose to CS2 but use Red Light (RL) to inhibit preselected neurons.
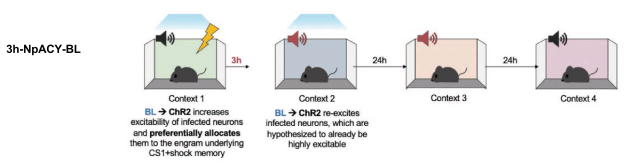
- Group 3h-NpACY-BL: Fear condition CS1 using blue light to bias preselected neurons towards inclusion in engram. 3 hours later, expose to CS2 but use Blue Light (BL) to similarly bias preselected neurons.
- Group 24h-NpACY-RL: Fear condition CS1 using blue light to bias preselected neurons towards inclusion in engram. 24 hours later, expose to CS2 but use Red Light (RL) to inhibit preselected neurons.
- Group 24h-NpACY-BL: Fear condition CS1 using blue light to bias preselected neurons towards inclusion in engram. 3 hours later, expose to CS2 but use Red Light (RL) to inhibit preselected neurons.
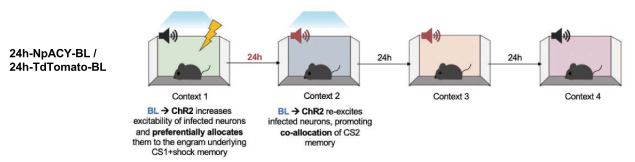
- Results
- 3 hours: optogenetically inhibiting, but not exciting, engram neurons impaired creation of freezing response to CS2
- 24 hours: optogenetically exciting, but not inhibiting, engram neurons created freezing response to CS2
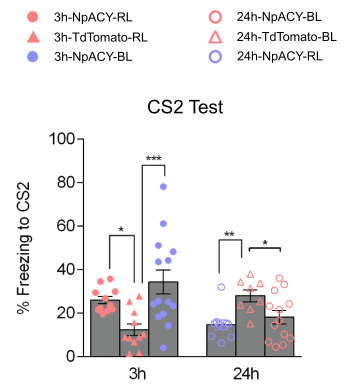
- 3 hour - Red light in 3 hour case impaired learning freezing response to CS1
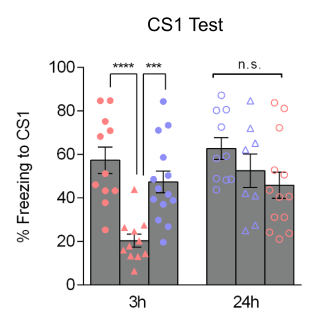
- Takeaway: persistent excitability is key for linking experiences in shared engram
Exp 6 (Neural, Behavioral)
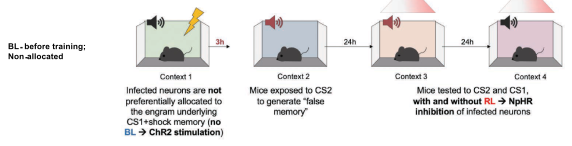
- Group 1: Blue light before CS1 fear conditioning. CS2 exposure after 3 hours. 24 hours later, test retrieval to CS2 (with or without red light, inhibiting selected neurons), then test retrieval to CS1 (with or without red light)
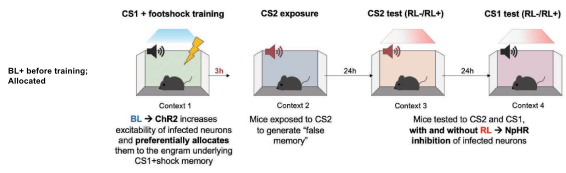
- Group 2: No blue light before CS
- Results:
- With blue light during CS1 conditioning and no red light during CS2 retrieval, high freezing
- With blue light during CS1 conditioning and red light during CS2 retrieval, low freezing
- With blue light during CS1 conditioning and red light during CS1 retrieval, low freezing
- Red light had no effect if no blue light used
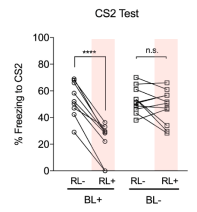
- Takeaway: Neutral stimulus is coallocated to the same engram as a negative stimulus if separated by 3 hours
- Freezing during red light + CS1 retrieval suggests CS1 and CS2 neurons are largely one and the same